Kannalife Sciences has focused its science on the research and development of a pipeline of next generation breakthrough therapeutics targeting inflammation.
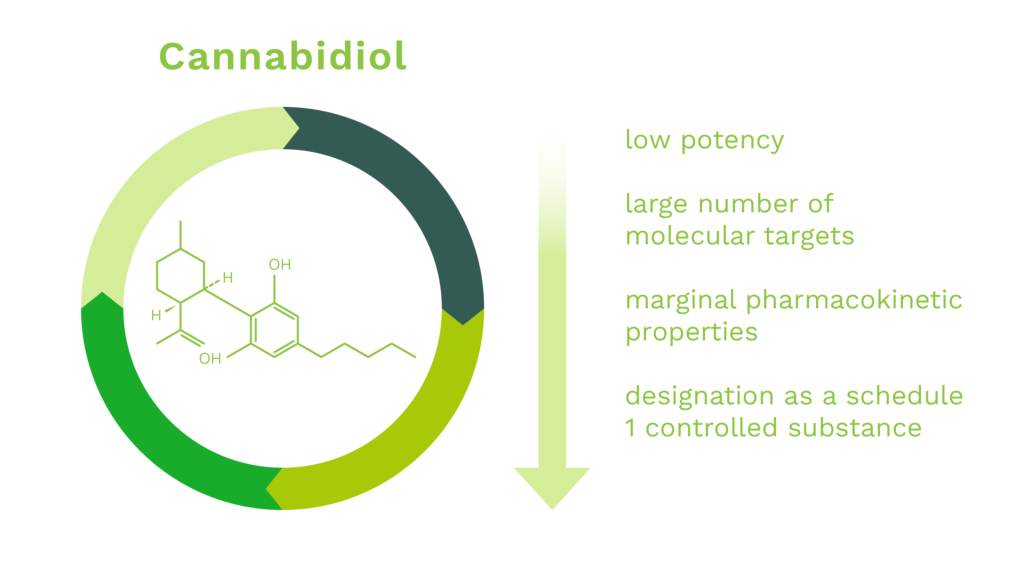
CBD is a naturally occurring cannabinoid constituent of cannabis. It was discovered in 1940 and is known to exhibit neuroprotective properties in many experimental systems. However, development of CBD as a drug has been confounded by the following issues:
To date there has been only one cannabidiol based medicament, Epidiolex™, approved for use in humans by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”). The drug, Epidiolex™, is used to treat seizures due to certain medical conditions (such as Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, Dravet syndrome). It is not known how this medication works for these seizures. Cannabidiol belongs to a class of drugs known as cannabinoids. Additionally, the FDA’s Office of Orphan Products Development (“OOPD”) has designated cannabidiol eighteen (18) times since 2013 for a multitude of diseases ranging from rare forms of epilepsy to prevention of reperfusion injury due to organ transplantation to glioblastoma multiforme to autoimmune hepatitis. While the Company’s primary indications of OHE and CIPN have not been targeted by CBD-based or CBD-derived drugs and cleared by the FDA or other foreign regulatory agency, neither have the aforementioned eighteen orphan designated indications targeted by cannabidiol.
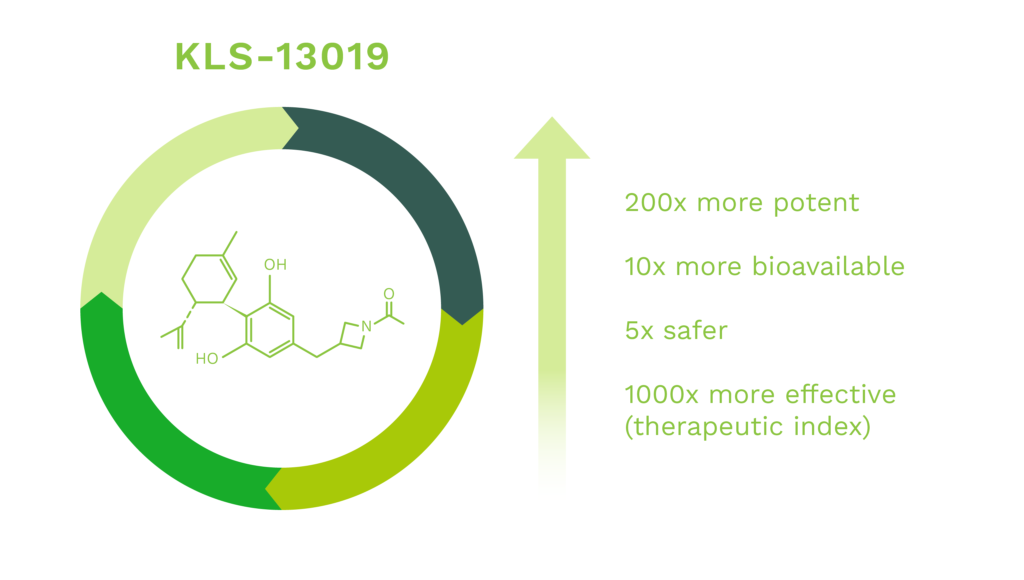
Kannalife’s present work has compared the properties of CBD with our patented novel cannabidiol derived molecule, KLS-13019, that has structural similarities to CBD. The design strategy for KLS-13019 was to increase hydrophilicity while optimizing neuroprotective potency against oxidative stress toxicity relevant to hepatic encephalopathy. In early pre-clinical studies, the responses of CBD and KLS-13019 were compared in dissociated rat hippocampal cultures in a pre-clinical model for overt hepatic encephalopathy (“OHE”) and chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (“CIPN”).
Therapeutics by the Numbers
We have made significant improvements in the chemistry efficacy and safety of our CBD-like molecules, lead by KLS-13019, that are up to 200X more potent, 10X more bioavailable, 5X safer and 1000 times more effective than CBD.
Our lead compound KLS-13019, is a first-in-class, novel IND enabled synthetic cannabinoid that has been validated through IND enabling studies to prevent and reverse chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN).
Peripheral neuropathy is a completely different class of pain, which is not the same as analgesic pain and mechanistically different. In addition to our drug’s ability to reverse peripheral neuropathy, animal studies have shown KLS-13019’s ability to reduce morphine reward seeking behavior.
CIPN is a neurodegenerative condition that afflicts patients undergoing chemotherapy with symptoms that include numbness, tingling, and pain and affects approximately 1/3 of patients undergoing chemotherapy cancer treatment. KLS-13019 can also be valuable as a potential alternative for opioid pain management.
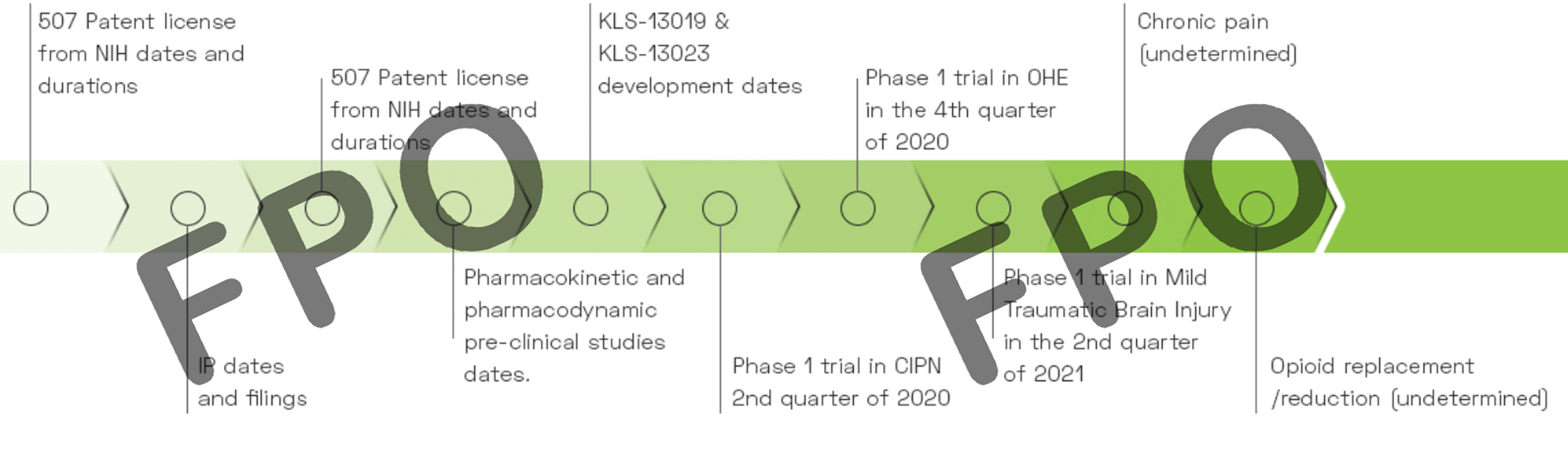
Kannalife Sciences has been awarded a total of $3,270,688 in study grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to date. The company was awarded a $299,916 study grant in 2018 from National Institute of Drug Abuse (NIDA) to research KLS-13019 for its development in Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy and Drug Dependence and in 2021 was awarded $2.97M in a 3-year IND enabling study grant with National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) to further research Development of KLS-13019 for Neuropathic Pain.
KLS-13019 have been published in more than 8 peer reviewed articles.
(1) ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters (2016, 7, 424-428) “Discovery of KLS-13019, a Cannabidiol-Derived Neuroprotective Agent, with Improved Potency, Safety, and Permeability”
(2) Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (14 August 2018) “Pharmacological Comparisons Between Cannabidiol and KLS-13019.”
(3) Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (10 May 2019) “Knockdown siRNA Targeting the Mitochondrial Sodium-Calcium Exchanger-1 Inhibits the Protective Effects of Two Cannabinoids Against Acute Paclitaxel Toxicity.”
(4) British Journal of Pharmacology (10 May 2019) “Behavioural and pharmacological effects of cannabidiol (CBD) and the cannabidiol analogue KLS-13019 in mouse models of pain and reinforcement.”
(5) Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (02 July 2022) “Anti-Inflammatory Properties of KLS-13019: a Novel GPR55 Antagonist for Dorsal Root Ganglion and Hippocampal Cultures.”
(6) Tetrahedron Letters (06 March 2023) “Efficient Syntheses of KLS-13019 Using Palladium Mediated Cross Couplings.”
(7) Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (June 2023) “GPR55 Antagonist KLS-13019 Reverses Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN) in Rats.”
(8) Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (11 April 2024) “Knockdown siRNA Targeting GPR55 Reveals Significant Differences Between the Anti‑inflammatory Actions of KLS‑13019 and Cannabidiol”
Pipeline
We are in the leadership role as a commercial drug discovery company advancing cannabinoid therapeutics to successfully synthesize CBD derived new chemical entities.
Intellectual Property
We have synthesized, pre-clincally tested and patented our proprietary CBD derived new chemical entities (“NCEs”), including KLS-13019 and also formulated a new CBD based molecule, KLS-13023. KLS-13019 is our lead target drug candidate and is part of an estate of new chemical entities (“NCEs”) underlying U.S. Patent 9,611,213 titled “Functionalized 1,3 Benzene-diols and their Method of Use for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy”. This patent is part of a divisional patent application by the Company to the USPTO whereby the Company sought separate claims for composition of matter, covered in Pat. 9,611,213 and separate claims for method of treatment; and U.S. Patent 10,004,722 titled “Method for Treating Hepatic Encephalopathy or a Disease Associated with Free Radical Mediate Stress and Oxidative Stress with Novel Functionalized 1,3 Benzene-diols.”
KLS-13019 and its related molecules describe novel functionalized 1,3-benzenediols and methods that may be useful and have potential for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy and related conditions. The present invention further describes a novel chemotype that may be useful and have potential for the treatment of diseases associated with hepatic encephalopathy. The present invention further describes a novel chemotype that may be useful and have potential as neuroprotective agents. The molecule portfolio under the present invention may be useful and have potential for treating and preventing diseases associated with free radical mediated stress and oxidative stress including, for example, as previously mentioned, hepatic encephalopathy, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s disease, traumatic head injury, stroke, epilepsy, neuropathic pain, Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE), Post Cardiac Arrest Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy, and Epileptic Encephalopathy.